Protection from Fire for Residential Homes in NZ
New building code changes are being proposed to improve fire protection for residential homes in New Zealand, particularly higher density housing.

Walls and structure within 1 metre of the boundary
The New Zealand building code looks to manage the spread of fire in residential buildings and outbuildings because this will help to protect life and property. New code changes are being considered and mainly relate to higher density housing.
Fire rating of walls close to a boundary
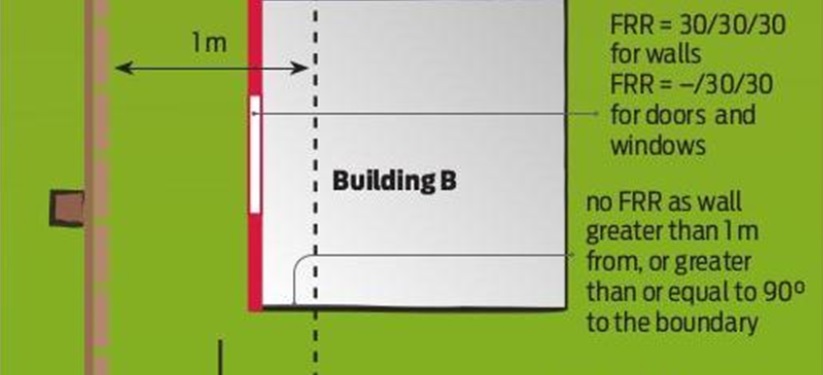
The Fire Resistance Rating (FRR) of a wall in a residential building in New Zealand must reach a minimum of 30/30/30 (structural adequacy/integrity/ insulation) from both sides of a wall when tested using MBIE protocols.
This is also referred to as 30-minute fire rating. It covers houses, townhouses, small multi-unit dwellings and limited-area outbuildings such as carports with walls less than 1 m from the boundary and angled at less than 90° to the boundary.
Acceptable Solution C/AS1
C/AS1 is a document first introduced by MBIE in 2012 and amended several times since. It is currently under review to allow for higher density buildings. C/AS1 covers the critical aspects of external fire spread:
- Fire spread across boundaries, affecting other property.
- Fire spread from lower roofs.
- External surface finishes, which are specified.
There are some exceptions:
- If you add a sprinkler system, then external walls do not need a fire-rated wall within 1m of a boundary.
- With walls less than 1m and sited at an angle less than 90° to the boundary, the wall parallel to the boundary must have an FRR of 30/30/30 from both sides of a wall. However, return walls that are 90° or more, even if they are within 1 m of the boundary, do not need an FRR (Figure 1). This exception is sometimes overlooked by designers, which would add more complexity and cost than necessary.
Windows and Doors and Services
Any windows and doors within walls that require FRR must also have FRR of -/30/30 (-/integrity/insulation).
This requirement also applies to service penetrations with some exceptions.

Intertenancy of walls and floors
The point of attention to fire ratings is for protection from risk for residents, stopping the spread of fire, but also for access by fire fighters and rescuers. As we move from low and low-medium density housing in NZ to higher density, we also have to re-design fire protection measures.
An inter-tenancy wall (ITW), common in Medium Density Housing (MDH), is a fire-resistant, sound-resistant, permanent legal structure between two adjoining properties. Usually going straight upwards from foundations to roof, an ITW can change position in both vertical and horizontal planes, although ideally, for simplicity’s sake, it won’t. The ITW denotes the legal boundary between adjoining properties, and because of this, it must not rely on support from either side that could be destroyed in a fire – it must be self-supporting.

Inter-tenancy floors (ITF) are also highly likely in multi-storey housing, with several MDH units placed vertically. These details are vitally important for fire safety and acoustic transmission, with detailing for fire compartmentalisation taking priority. Stopping fire from moving outside of the housing unit is called passive fire protection. To ensure passive fire protection is effective, each dwelling unit’s entire inter-tenancy structure (including common walls, ceiling and floor and walls separating the dwelling from an escape route) must be fire-resistant. This is really important when installing services, as a boundary is no longer fire-resistant if penetration is made and not adequately fire-stopped.
A common scenario is that a wall is properly constructed to a tested, fire-resistant specification, but subsequent running of services such as plumbing, electrical, internet, gas and air conditioning compromises that fire-resistance by cutting a hole in the wall. The fire-resistant construction needs to extend and meet at each junction between walls, ceilings and floors.

External walls
Externally, there are further requirements. MDH design should consider three potential vertical fire spread mechanisms for external walls:
- fire spread through wall openings
- combustibility of the cladding system
- fire spread from lower roofs.
It can be taken that fire spread vertically on the exterior of a high-rise residential building is acceptable for one storey but not if it reaches higher.

Author: Stewart Hobbs - Principal Engineer at ProConsult
Stewart is the journal editor for SESOC (Structural Engineering Society New Zealand (Inc.)








